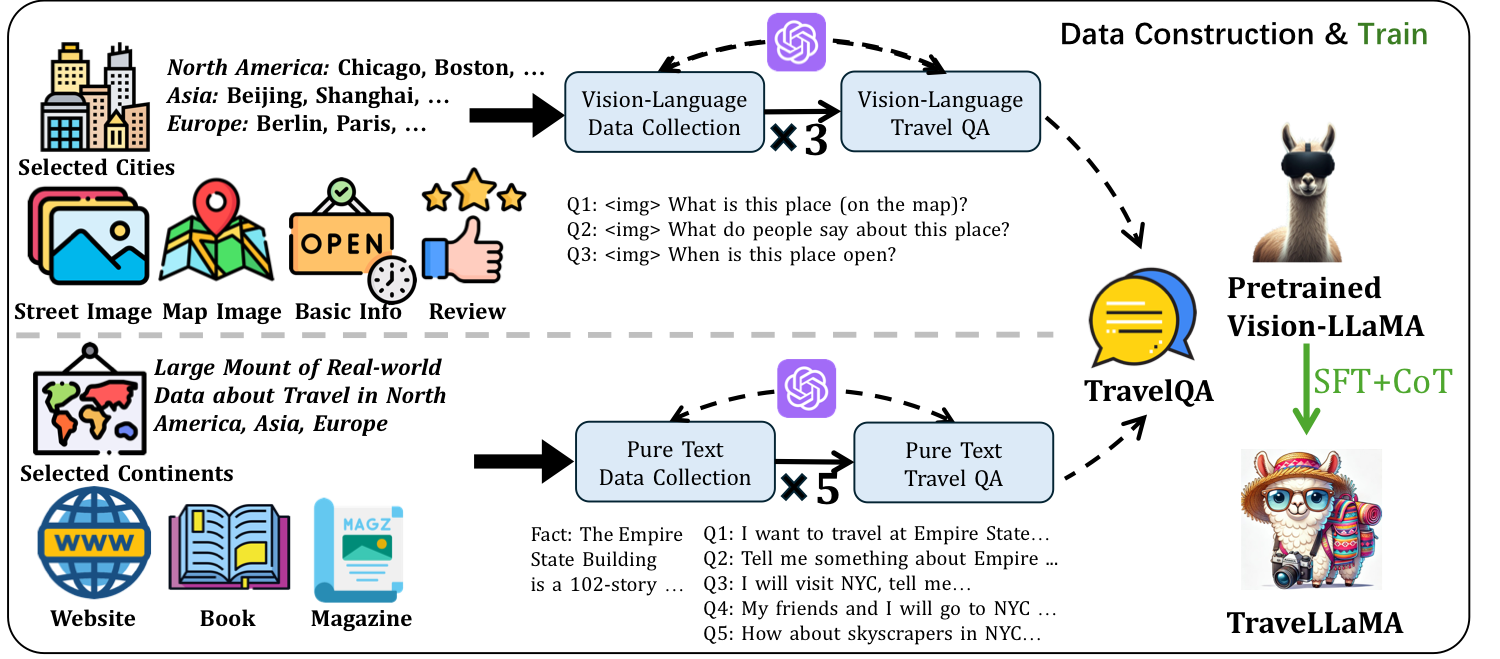
Tourism and travel planning increasingly rely on digital assistance, yet existing multimodal AI systems often lack specialized knowledge and contextual understanding of urban environments. We present TraveLLaMA, a specialized multimodal language model designed for comprehensive travel assistance. Our work addresses the fundamental challenge of developing practical AI travel assistants through three key contributions:
(1) TravelQA, a novel dataset of 265k question-answer pairs combining 160k text QA from authentic travel sources, 100k vision-language QA featuring maps and location imagery, and 5k expert-annotated Chain-of-Thought reasoning examples; (2) Travel-CoT, a structured reasoning framework that decomposes travel queries into spatial, temporal, and practical dimensions, improving answer accuracy by 10.8% while providing interpretable decision paths; and (3) an interactive agent system validated through extensive user studies.
Through fine-tuning experiments on state-of-the-art vision-language models, we achieve 6.2-9.4% base improvements, further enhanced by Travel-CoT reasoning. User studies with 500 participants show TraveLLaMA achieves a System Usability Scale score of 82.5, significantly outperforming general-purpose models.
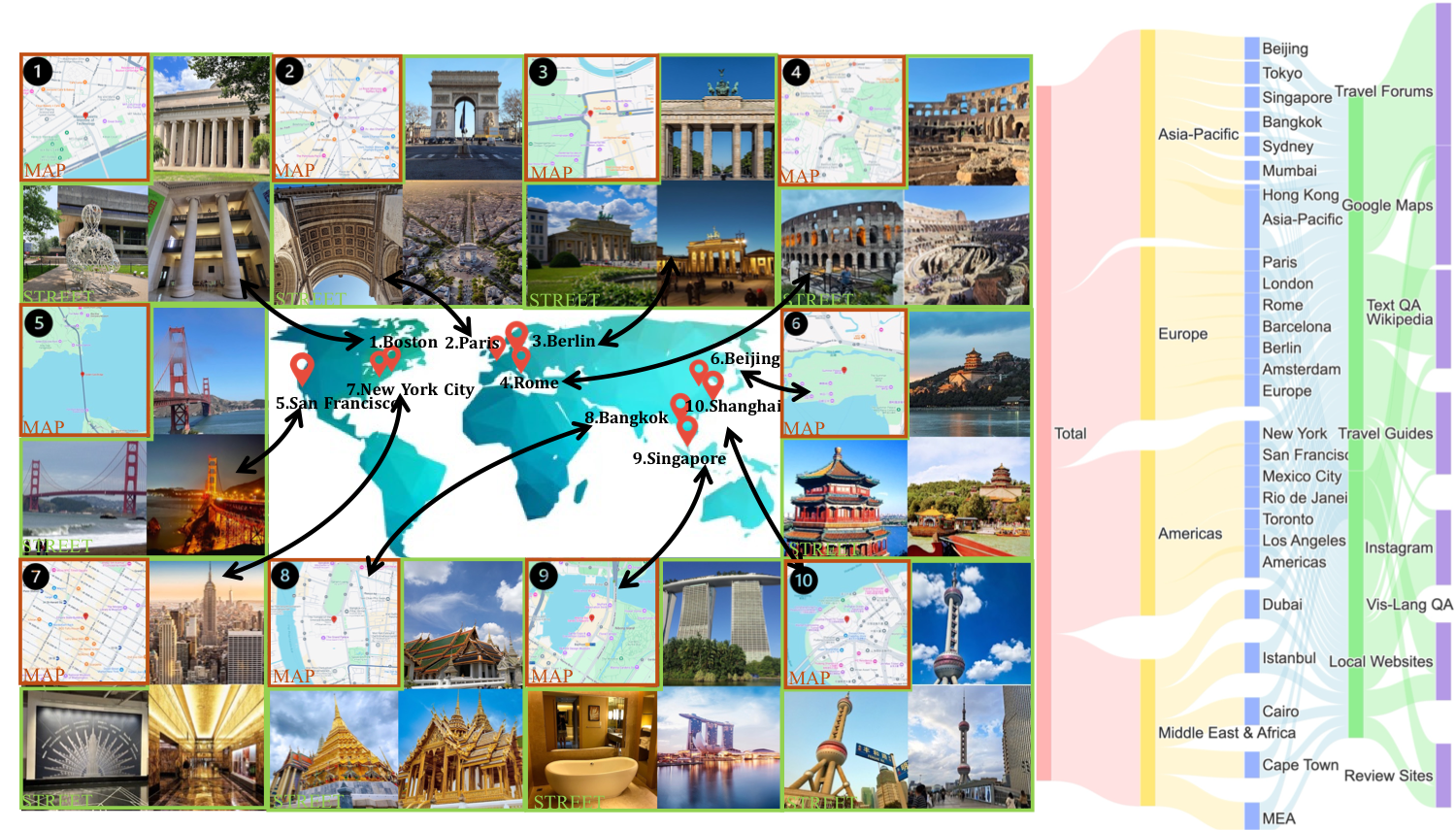
The first large-scale multimodal travel dataset spanning 35+ cities worldwide
Three major innovations for advancing AI-powered travel assistance
The first large-scale multimodal travel dataset with 265k QA pairs: 160k text-based pairs from travel forums, 100k vision-language pairs with maps and photos, and 5k expert-annotated CoT reasoning examples across 35+ cities.
A structured reasoning framework that decomposes queries into spatial, temporal, and practical dimensions. Beyond 6.2-9.4% base improvements, Travel-CoT achieves an additional 10.8% accuracy gain with interpretable reasoning paths.
A ReAct-based agent that integrates real-time services for dynamic planning. Validated by 500 users with a SUS score of 82.5 (Excellent), demonstrating superior usability for complex travel planning tasks.
Decomposing travel queries into interpretable reasoning dimensions
Real-time planning with iterative reasoning and tool integration

Comprehensive evaluation on TravelQA benchmark
| Method | LLM Backbone | Pure Text | VQA | Full Score | Δ Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLIP-2 | Vicuna-13B | 60.3 | 51.6 | 56.9 | — |
| InstructBLIP | Vicuna-13B | 64.6 | 55.4 | 61.1 | — |
| Shikra | Vicuna-13B | 71.6 | 60.8 | 67.5 | — |
| Qwen-VL | Qwen-7B | 72.1 | 61.6 | 68.1 | — |
| LLaVA-1.5 | Vicuna-13B | 74.3 | 63.3 | 70.0 | — |
| Fine-tuned on TravelQA | |||||
| Qwen-VL (ft) | Qwen-7B | 78.7 | 67.7 | 74.5 | +9.4% |
| LLaVA-1.5 (ft) | Vicuna-13B | 80.4 | 68.9 | 76.0 | +8.6% |
| TraveLLaMA (Ours) | Vicuna-13B | 82.5 | 70.5 | 77.8 | +10.8% |
System Usability Scale (SUS) evaluation with 500 participants
Our user study demonstrates that TraveLLaMA significantly outperforms general-purpose models in travel planning tasks. The 6.2-point SUS improvement is driven by domain-optimized design, reflected in strong ease-of-use, learnability, and reduced-complexity ratings. Users consistently found TraveLLaMA more intuitive and less cognitively demanding for travel planning.
TraveLLaMA vs. Claude 3.5 on real-world travel queries

Key Observations: TraveLLaMA consistently outperforms Claude 3.5 in accuracy and contextual understanding:
@inproceedings{chu2026travellama,
title = {TraveLLaMA: A Multimodal Travel Assistant with Large-Scale Dataset and Structured Reasoning},
author = {Chu, Meng and Chen, Yukang and Gui, Haokun and Yu, Shaozuo and Wang, Yi and Jia, Jiaya},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
year = {2026}
}